In today’s global economy, importing from China has become a strategic move for businesses seeking competitive advantage through cost-effective manufacturing and various products. However, navigating the complex landscape of international trade is challenging; you should know the risks of importing from China. In this article, we will explore the import risks from China—including quality control, supply chain disruptions, and regulatory hurdles—and provide import risk management insights on mitigating these risks to ensure a smooth and profitable import experience.
Part 1: Identifying the Risks of Importing from China
Quality Issues
Substandard Products: Substandard products fail to meet the essential quality criteria the buyer sets or the industry standards. These products can pose significant risks, including safety hazards, decreased customer satisfaction, and damage to brand reputation. The reasons behind substandard production, including using inferior materials, poor workmanship, or inadequate quality control processes, can vary.
Inconsistent Quality: Inconsistent quality refers to the variability in product standards between different batches or even within the same batch. This inconsistency can undermine consumer trust and lead to higher return rates, affecting the bottom line and brand reputation. Causes of inconsistent quality may include fluctuations in raw materials, changes in production processes, or lack of skilled labor.
Lack of Adherence to Specifications: Adhering to specified quality standards and regulatory requirements is crucial in maintaining product legality and customer trust. Non-compliance can lead to legal issues, product recalls, and severe brand damage.
Here is an bad review of duvets we found from other sellers.
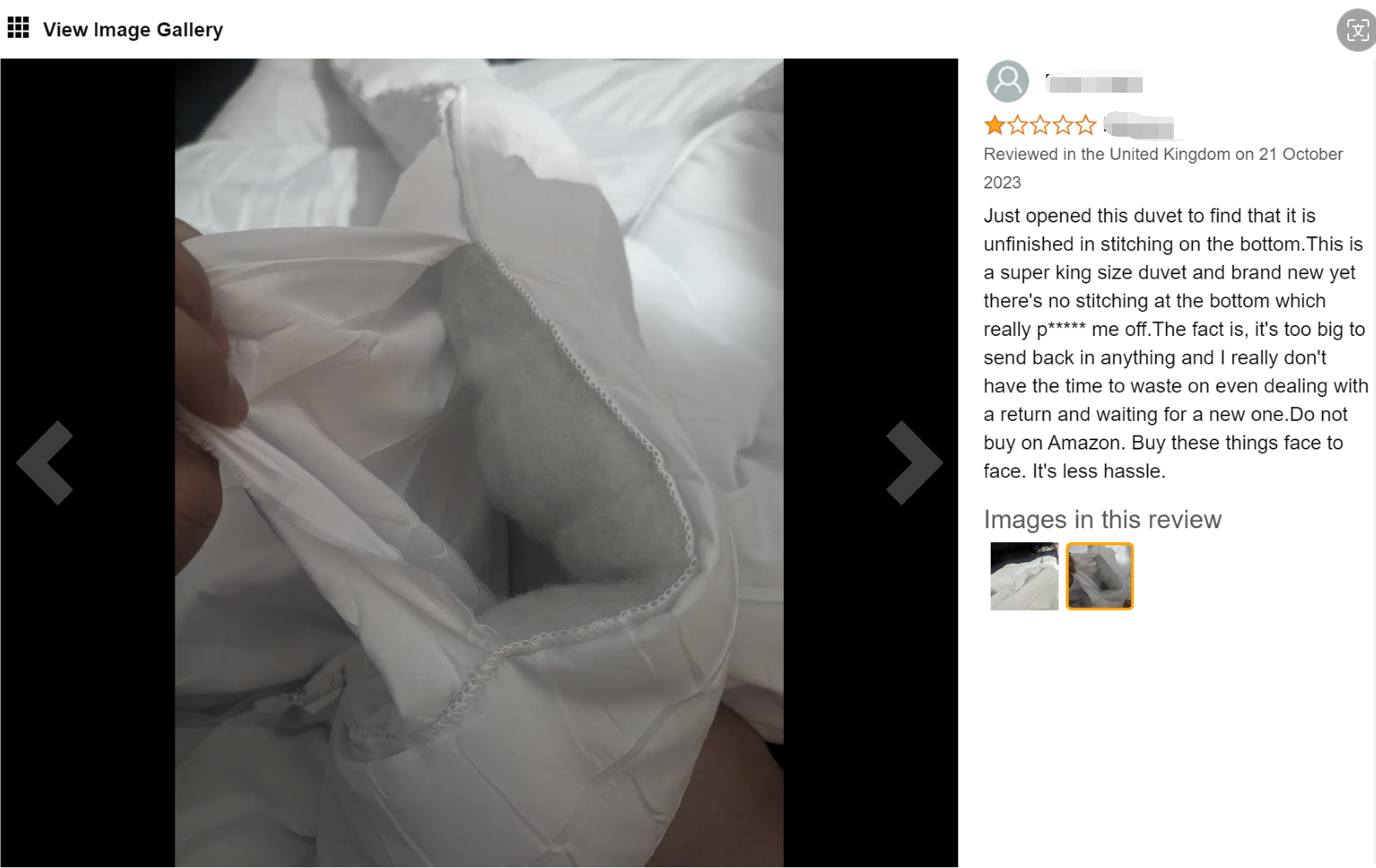
Supply Chain and Logistics Risks
Delays in Shipment:
Customs and Regulatory Delays: Often, goods can be held up due to stringent customs regulations or unexpected changes in import/export policies.
Manufacturing Delays: Issues at the manufacturing level, such as raw material shortages or workforce disruptions, can lead to delays before the goods are shipped.
Transportation Issues: Problems like limited availability of shipping containers, strikes at ports, or disruptions in transportation routes (due to political situations or natural disasters) can also cause delays.
Damage During Transit:
Inadequate Packaging: Poor or insufficient packaging can lead to damage, especially for fragile goods.
Handling Issues: Rough handling during loading, unloading, or transit can cause damage. This is mainly a risk with frequent transloading of goods.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to extreme weather conditions, humidity, or other environmental factors during transit, especially over long sea voyages, can damage goods.
Loss of Goods:
Misplacement or Mislabeling: Human errors in labeling or tracking can lead to goods being lost or sent to the wrong destination.
Insolvency of Carriers: If a shipping company faces financial issues and ceases operations, goods in transit might be held indefinitely or lost.

Regulatory and Compliance Risks
Import Regulations and Customs
When importing from China, adhering to import regulations and customs rules is crucial. Businesses must understand tariffs, taxes, and restrictions and prepare for potential delays caused by complex customs procedures.
Safety and Certification Standards
Products from China must meet the safety and quality standards of the destination country. Risks of non-compliance include rejecting goods, legal penalties, and reputation damage.
Intellectual Property Violations
There is a risk of intellectual property violations when importing goods, leading to legal issues and brand damage. Customs authorities have the right to detain and destroy goods that infringe on intellectual property, resulting in financial loss and supply chain disruptions. Continuous intellectual property violations may lead to specific markets or channels refusing a company’s products.

Financial Risks
Payment Frauds:
Importing from China involves financial transactions, and payment frauds are a significant concern. Scams may include false invoicing, non-existent products, or deceptive payment channels.
Currency Exchange Volatility:
Fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact the overall cost of imported goods. Sudden changes in the value of the Chinese Yuan against your local currency may lead to unexpected expenses or reduced profit margins.
Hidden Costs (e.g., taxes, duties):
Beyond the product cost, there are often hidden expenses associated with importing from China. Taxes, duties, and other regulatory fees can significantly affect the final landed cost of goods.
Part 2: How to Reduce the Risks
Improving Quality Control
-
Clear Product Specifications:
Emphasize the need for detailed, comprehensive product specifications to ensure mutual understanding and meet quality expectations.
Make sure every detail is written clearly in the contract.
For example, for our fleece blanket, the below information needs to be cleared in the contract:
Gsm weight, net weight/pc, sizes, wash label requirement, packaging requirement, shipping marks, etc., Amazon requests each carton length not exceed 63cm and carton gross weight less than 20kgs.
-
Pre-shipment Inspections:
Highlight the importance of inspecting products before shipping from China to identify and resolve issues early.
Discuss options like random sampling or complete checks and the process of arranging these inspections, including using third-party inspection.
Usually, we do self-inspection during the whole production process. For example, for our microfiber duvets, we make the following for quality control:
Check the gsm weight and softness of the polyester fabric during weaving.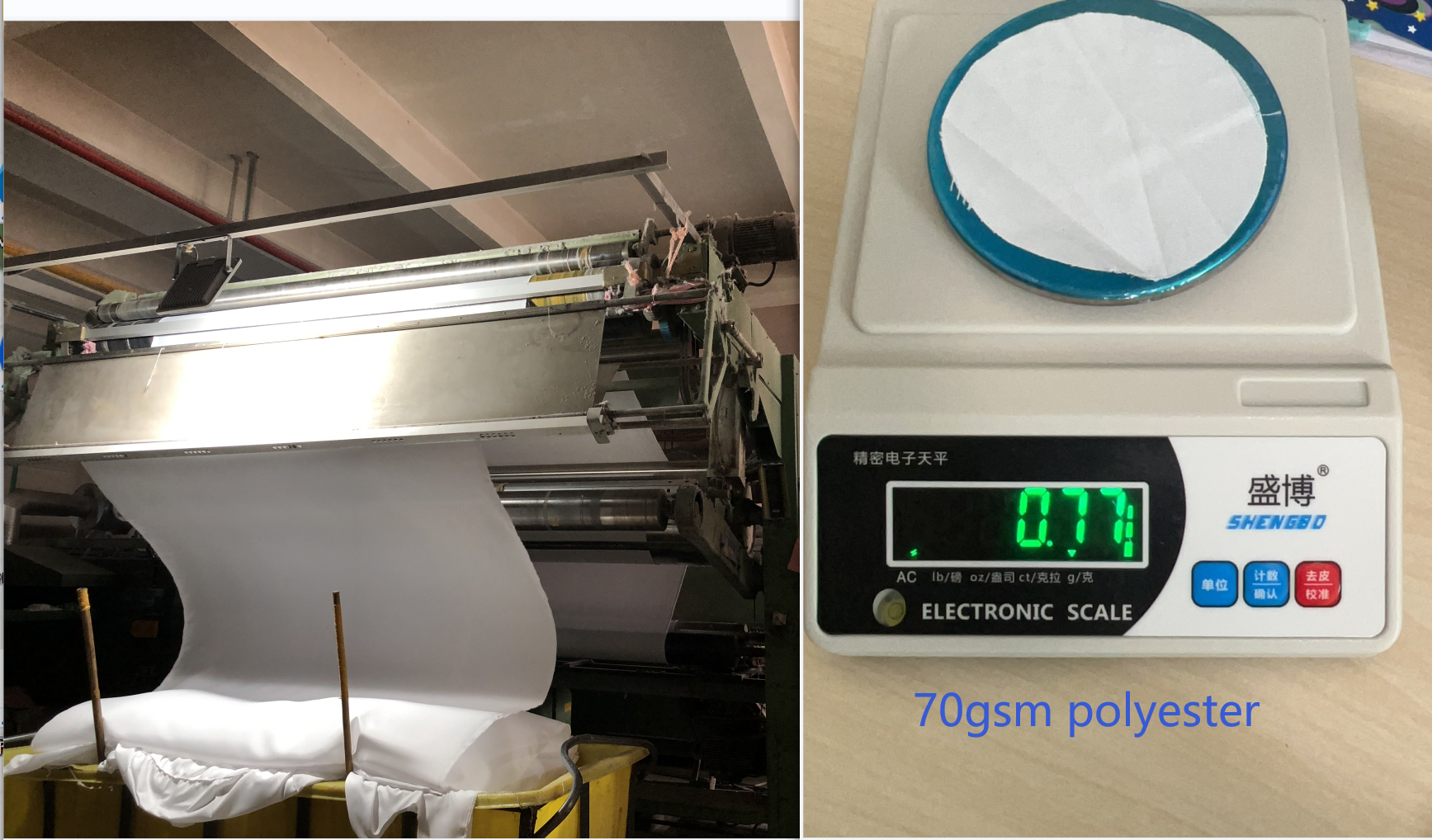
Check the filling hollow fiber gsm weight and material during production.
Checking each production process: box quilting, edge wrapping, etc.
The quality control team reviews the size, weight, and stain before packaging.

-
Regular Supplier Audits:
Stress the necessity of regular audits to assess supplier adherence to quality standards and ethical practices.
Outline the audit process, frequency, and how to use findings to continuously improve supplier relationships and product quality.
Streamlining Supply Chain and Logistics
-
Reliable Freight Forwarding Partners
· Choose partners with deep knowledge of Chinese export laws and international shipping
· Value a network that offers smooth shipment handling and problem-solving skills.
· Look for technology integration for real-time shipment tracking and management.
-
Insurance Coverage
· Understand different insurance types (cargo, liability, etc.) and their benefits.
Conduct a thorough risk assessment to determine appropriate coverage.
Be aware of the insurance claims process and perform a cost-benefit analysis.
- Diversified Shipping Routes
Analyze and choose shipping routes based on reliability, cost, and speed.
Diversify routes to mitigate geopolitical and natural risks.
Balance cost-effectiveness with efficiency and have flexible shipping plans.
We have been doing exportation for 10+ years; we work with many logistics companies that can handle customs clearance, FBA fulfillment, etc. Which can help save you time and money.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
- Understanding Import Laws:
Being well-informed about both Chinese export regulations and the destination country’s import laws.
When signing the contract, highlight critical areas such as tariffs, trade agreements, and restricted or prohibited items.
Consulting with trade experts or legal advisors to navigate complex legal frameworks effectively.
- Ensuring Product Certifications:
Discuss the necessity of obtaining the correct certifications that attest to the quality and safety of products.
Discuss in detail the standard certifications that are required for different types of products, like electronics or consumer goods.
Working closely with suppliers to ensure all products meet the necessary standards and certifications before shipping.
We are applying for the OEKO-TEX standard 100 certificates for fleece blankets, duvets, blanket hoodies, etc. We will get it by the beginning of March.

- Protecting Intellectual Property Rights:
Safeguarding intellectual property (IP) when importing from China.
Register and protect IP rights in China, including patents, trademarks, and copyrights.
Monitor and enforce IP rights, such as conducting regular market surveys and working with local legal experts.
Managing Financial Exposure
- Secure Payment Methods (e.g., Letter of Credit):
For big orders, you can consider L/C payment terms.
For new suppliers, you can consider payment step by step. For example 15% deposit in advance, after supplier showing the materials, another 15% deposit to be paid.
- Hedging Currency Risk:
Managing currency fluctuation risks in international trade.
There are some payment company, like Pingpong, X-transfer, they can support multiple currency which can reduce currency fluctuation risks.
Here is the link for X-transfer, you can check more details.
https://www.xtransfer.cn/?lang=en
If you think this article is helpful, please share it with your friends and leave your ideas in the comments section. If you have any inquiry, please CONTACT US.



